Alveolar Ridge Preservation and Augmentation for Optimal Implant Placement
Course Number: 626
Course Contents
Planning Ridge Augmentation Based on Edentulous Site Evaluation
An edentulous site planned for implant therapy, once evaluated clinically and radiographically, can be classified using one of the many published classifications. This will help the clinician decide on whether the site can be grafted simultaneously during implant surgery or a staged approach should be implemented. Below is one such example of a classifications system, proposed by Benic et al, for implant planning of an edentulous site.26 The proposed treatment recommendations, though, should be considered in lieu of other factors such as bone quality, anatomic limitations, patient factors and clinician’s expertise.
Table 1.
| Bone Defect | Description | Proposed Treatment Recommendations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 0 | 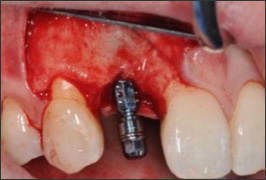 | Site with ridge contour deficit and sufficient bone volume for standard implant placement | • Simultaneous implant placement • GBR with resorbable membrane and particulate graft |
| Class 1 | 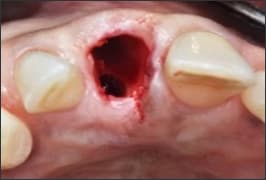 | Intra-alveolar defect between the implant surface and intact bone walls (limited to situations where immediate implant placement is performed) | In esthetically sensitive site: • Use bone substitute into the intra-alveolar defect and over the buccal bone wall and coverage with resorbable membrane In esthetically non sensitive site when the horizontal defect dimension is >1-2 mm: • Application of bone substitute into the intra-alveolar defect and coverage with resorbable membrane |
| Class 2 | 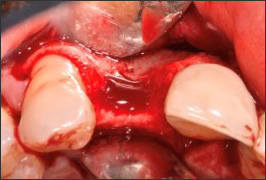 | Peri-implant dehiscence, in which the volume stability of the area to be augmented is provided by the adjacent bone walls | • Simultaneous implant placement • GBR with resorbable membrane and particulate graft |
| Class 3 | 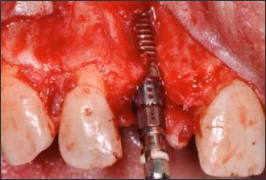 | Peri-implant dehiscence, in which the volume stability of the area to be augmented is not provided by the adjacent bone walls | • Simultaneous implant placement • Use of rigid barrier membrane such as ePTFE along with particulate bone substitute for GBR |
| Class 4 | 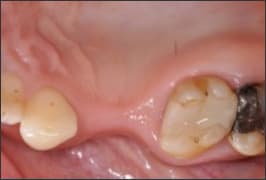 | Horizontal ridge defect requiring bone augmentation before implant placement | • Staged implant placement • Augmentation with any of the following methods: 1. Autogenous bone blocks 2. ePTFE or Titanium mesh with particulate bone substitute 3. Distraction osteogenesis 4. Ridge split techniques |
| Class 5 | 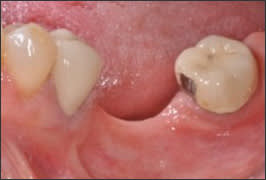 | Vertical ridge defect requiring bone augmentation before implant placement | • Staged implant placement: 1. Autogenous bone blocks 2. ePTFE or Titanium mesh with particulate bone substitute 3. Distraction osteogenesis |
Adapted from Benic et al, Periodontology; 2000.26
One other simplistic way of classifying edentulous ridges is the one suggested by Seibert et al.27 in 1983:
Class I – buccolingual loss of tissue with normal apico-coronal height
Class II – apico-coronal loss of tissue with normal buccolingual ridge width
Class III – combination type defects (loss of both height and width)

